



Next: Transitive Sentential Subject: Ts0Vnx1
Up: Verb Classes
Previous: Sentential Complement: Tnx0Vs1
Intransitive with Adjective: Tnx0Vax1
- Description:
- The verbs that select this tree family take an adjective
as a complement. The adjective may be regular, comparative, or superlative.
It may also be formed from the special class of adjectives derived from the
transitive verbs (e.g. agitated, broken). See
section 6.2). Unlike the Intransitive with PP verbs (see
section 6.10), some of these verbs may also occur as bare
intransitives as well. This distinction is drawn because adjectives do not
normally adjoin onto sentences, as prepositional phrases do. Other
intransitive verbs can only occur with the adjective, and these select only
this family. The verb class is also distinguished from the adjective small
clauses (see section 6.20) because these verbs are not raising
verbs. 34 verbs select this tree family.
- Examples:
- become, grow, smell
The greenhouse became hotter .
The plants grew tall and strong .
The flowers smelled wonderful .
- Declarative tree:
- See Figure 6.13.
Figure:
Declarative Intransitive with Adjective Tree: 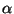 nx0Vax1
nx0Vax1
|
|
- Other available trees:
- wh-moved subject, wh-moved adjective
(how), subject relative clause with and without comp,
adjunct (gap-less) relative clause with comp/with PP pied-piping, imperative, NP gerund.




Next: Transitive Sentential Subject: Ts0Vnx1
Up: Verb Classes
Previous: Sentential Complement: Tnx0Vs1
XTAG Project
1998-09-14